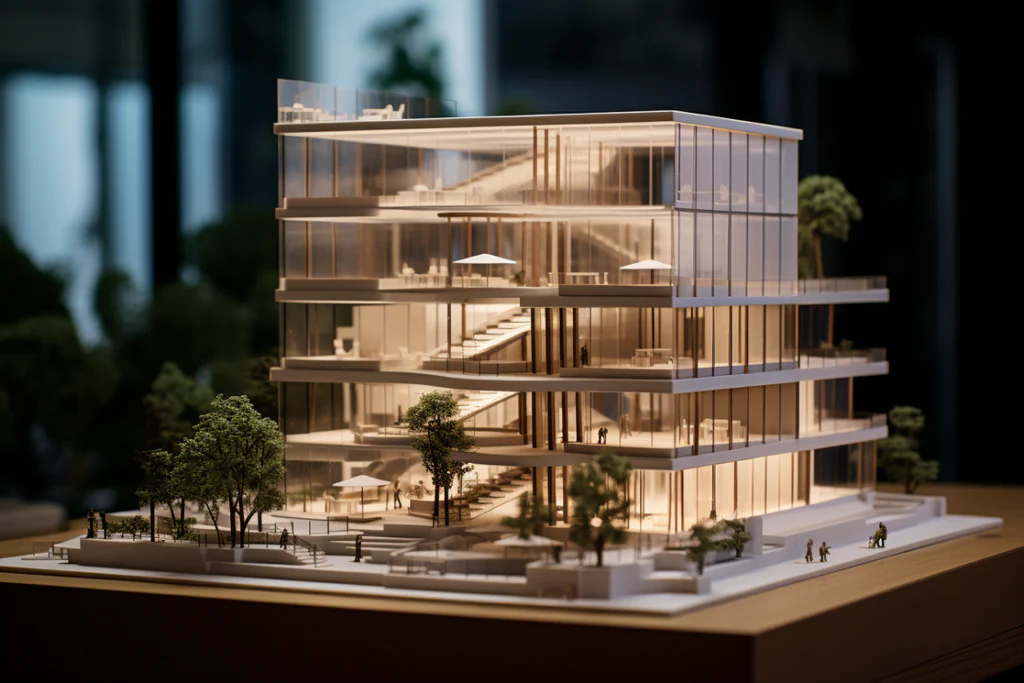
In the realm of architecture, visualization plays a crucial role in transforming concepts into tangible realities. Traditionally, architects have relied on physical models, sketches, and digital renderings to communicate their designs. However, advancements in 3D printing technology, particularly resin 3D printing, have introduced a new dimension to architectural visualization. Resin 3D printing offers precision, detail, and versatility that are unmatched by other methods, making it an invaluable tool for architects and designers. Here’s how resin 3D printing is revolutionizing architecture visualization.
1. High-Resolution Detailing
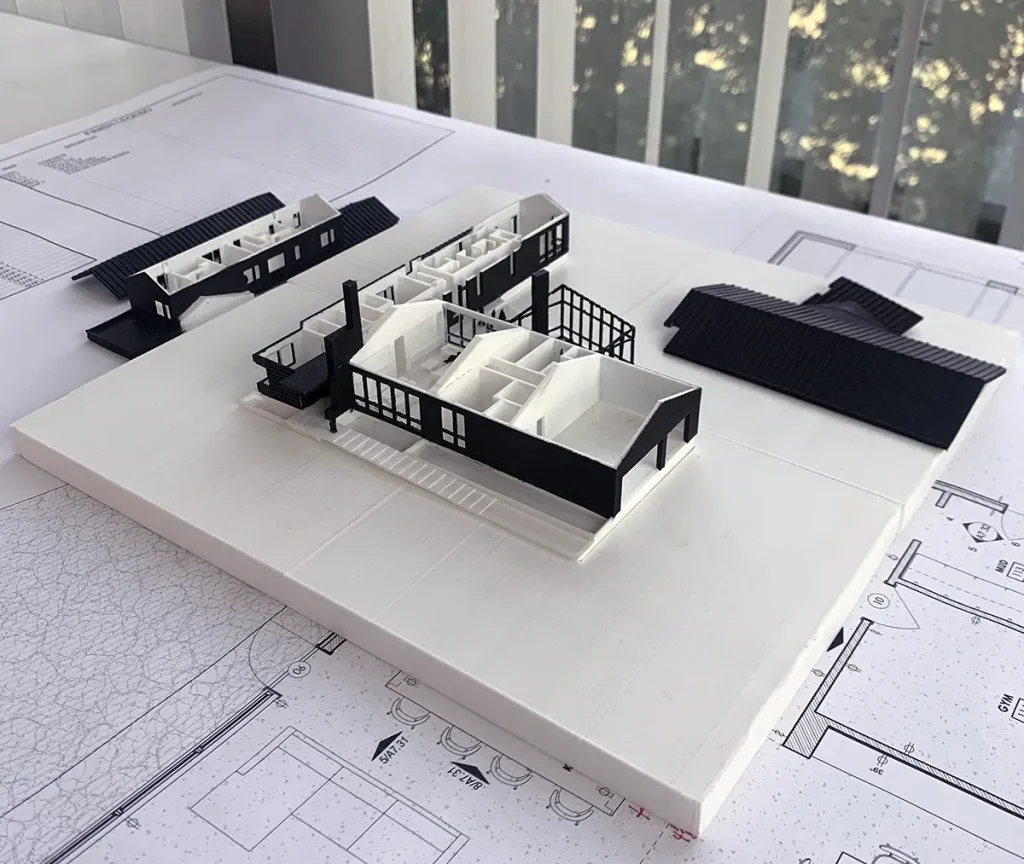
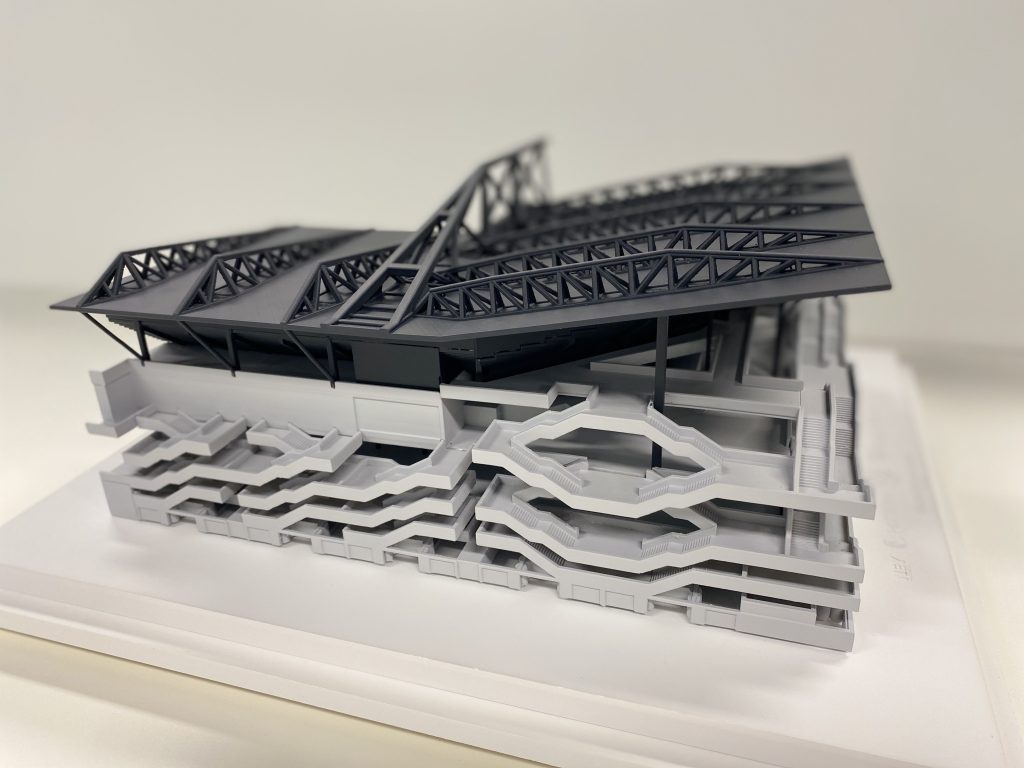
One of the standout features of resin 3D printing is its ability to produce highly detailed models with smooth surfaces and intricate geometries. Unlike Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), which uses thermoplastic filaments, resin 3D printers use photopolymer resins that are cured layer by layer using UV light. This process allows for extremely fine layers, often as thin as 25 microns, resulting in models with exceptional resolution.
For architects, this means that even the most intricate details of a design—such as façade textures, window frames, and ornamental elements—can be accurately replicated in the physical model. This level of detail is essential for accurately conveying the aesthetics and functionality of a building, especially when presenting to clients, stakeholders, or planning committees.
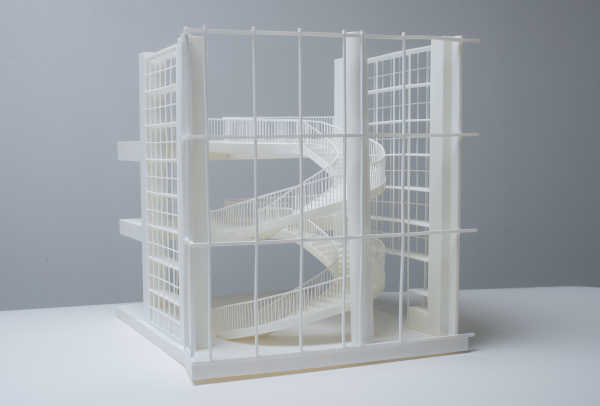

2. Enhanced Design Communication
Resin 3D printing enhances the communication of architectural designs by providing a physical model that can be easily understood by clients who may not be familiar with reading blueprints or digital renderings. A physical model allows clients to better visualize the scale, proportion, and spatial relationships of a project, leading to more informed decision-making.
Moreover, resin 3D printed models can be produced in a variety of scales, from large-scale site models to small-scale detail studies. This versatility allows architects to focus on different aspects of the design, whether it’s the overall massing of a building or the specific details of an interior space. By holding a tangible model, clients can gain a clearer understanding of the architect’s vision, facilitating more productive discussions and reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings.
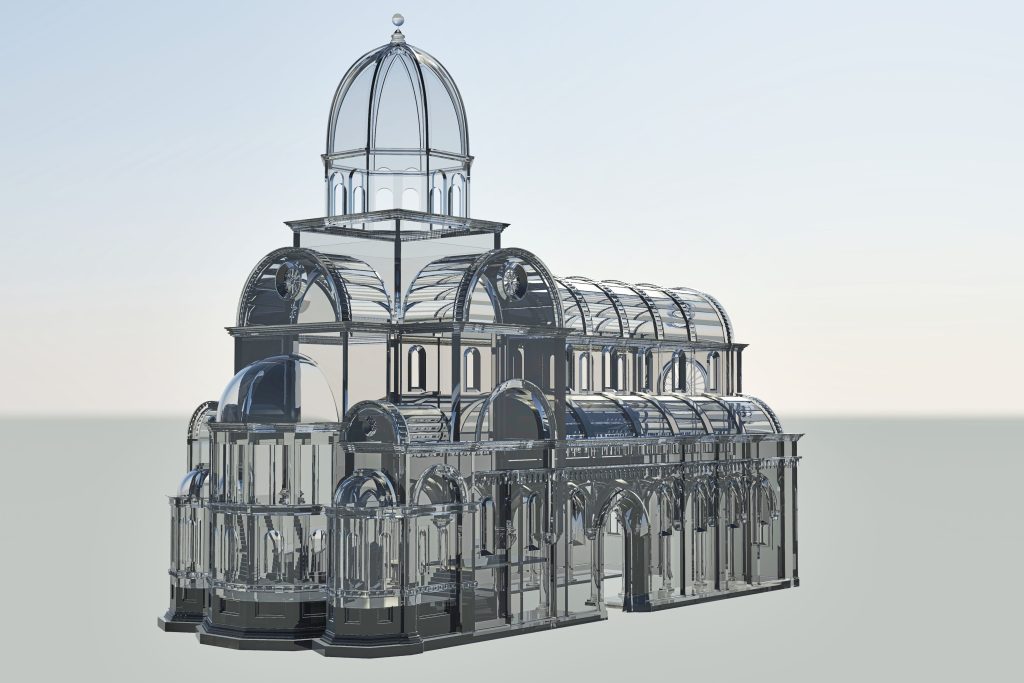

3. Material Versatility and Customization
Resin 3D printing offers a wide range of material options, each with different properties that can be tailored to the specific needs of an architectural model. For example, standard resins provide a balance of strength and detail, making them ideal for general-purpose architectural models. On the other hand, clear resins can be used to create transparent elements, such as glass windows or skylights, adding an extra layer of realism to the model.
In addition to standard materials, there are also resins with special properties, such as flexible resins that can simulate soft materials like rubber or resin blends that mimic the appearance of concrete or wood. This material versatility allows architects to create models that not only look like the final building but also behave like the intended materials, providing a more accurate representation of the design.
4. Rapid Prototyping and Iteration
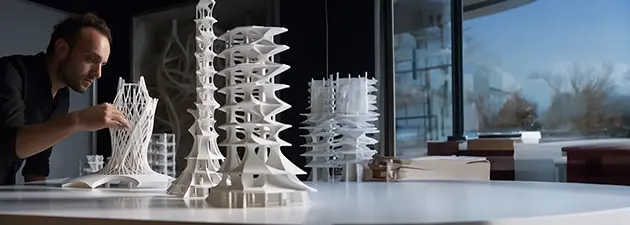
One of the significant advantages of 3D printing in general, and resin 3D printing in particular, is the ability to quickly produce prototypes and iterate on designs. In the fast-paced world of architecture, where timelines are often tight, the speed of resin 3D printing can be a game-changer.
Architects can quickly produce a model, evaluate it, and make necessary adjustments to the design. This rapid prototyping capability allows for more experimentation and innovation, as changes can be made and tested in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional model-making techniques. The ability to quickly iterate on designs not only improves the final outcome but also reduces the overall cost and time associated with the project.

5. Cost-Effective Production
While traditional architectural model-making often requires skilled labor and expensive materials, resin 3D printing offers a more cost-effective solution. Once the initial investment in a 3D printer and materials is made, the cost of producing additional models is relatively low. Resin printers are also capable of producing complex designs that would be difficult or costly to achieve by hand, further reducing the need for specialized labor.
Additionally, resin 3D printing minimizes material waste, as only the necessary amount of resin is used for each print. This efficiency not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainable practices, making resin 3D printing an eco-friendly option for architectural visualization.
6. Integration with Digital Design Tools
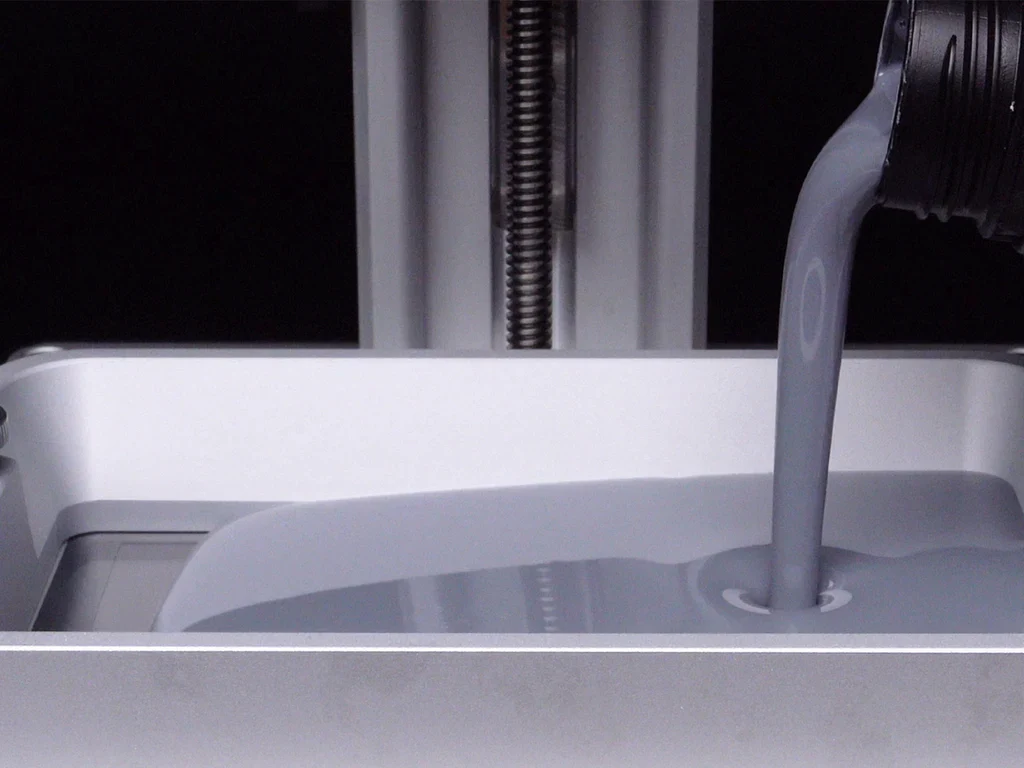
Resin 3D printing seamlessly integrates with digital design tools commonly used in architecture, such as CAD software and Building Information Modeling (BIM). Architects can easily export their digital models to a 3D printer, enabling a smooth transition from the design phase to physical model production. This integration also allows for the easy updating of models as the design evolves, ensuring that the physical representation is always up-to-date.
Moreover, the ability to print directly from digital files reduces the risk of errors that can occur when translating a design from paper to a physical model. The result is a more accurate and reliable representation of the architect’s vision.
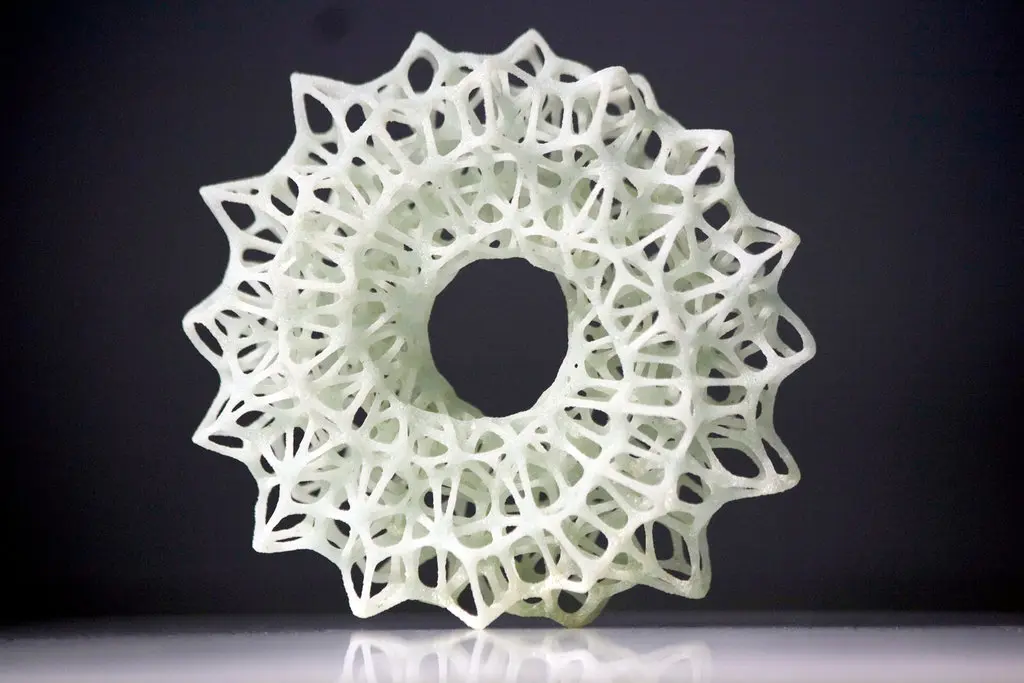

7. Bringing Concepts to Life
Perhaps the most significant benefit of resin 3D printing in architecture is its ability to bring concepts to life in a tangible form. While digital renderings and virtual reality models offer impressive visualization capabilities, there is something uniquely powerful about holding a physical model. It allows architects, clients, and stakeholders to engage with the design in a more intuitive and immediate way.
For educational purposes, resin 3D printing also provides architecture students with the opportunity to explore their designs in the physical world. This hands-on experience is invaluable for understanding scale, proportion, and spatial relationships—key concepts that are sometimes difficult to fully grasp through digital means alone.
Resin 3D printing is transforming the field of architecture visualization by offering unparalleled precision, material versatility, and cost-effective production. Whether for professional practice or academic exploration, this technology empowers architects to create detailed, realistic models that enhance design communication and bring architectural concepts to life. As resin 3D printing technology continues to advance, its role in architecture is likely to expand, further pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in architectural visualization.










